Calycanthus Floridus: A Detailed Overview


Intro
Calycanthus floridus, commonly known as sweetshrub or Carolina allspice, stands tall as a cherished specimen in the botanic landscape of the southeastern United States. This plant not only boasts attractive flowers but also has a significant footprint in the ecosystem it inhabits. Understanding the nuances of its growth habits and environmental needs can aid ecologists, conservationists, and landscape enthusiasts alike. In this article, the various dimensions of Calycanthus floridus will be explored—from its unique biological features to its historical background and ecological relevance.
Before delving deeper, it is crucial to touch upon the broader context in which this species thrives: forestry practices. This sets the stage for discussing sustainable management and woodland stewardship practices that can help integrate Calycanthus floridus into broader ecological frameworks.
Overview of Forestry Practices
Definition of Forestry
Forestry refers to the science, art, and practice of managing forests, tree plantations, and related resources for various purposes. This includes production of wood, biodiversity conservation, and recreation among others. The interaction between human activities and forest ecosystems shapes the management practices employed in this field. These practices are pivotal not just for conserving natural landscapes but also for maintaining a good balance within ecosystem dynamics.
Importance of Forestry in Ecosystem Management
Forestry plays a vital role in ecosystem management for several reasons:
- Biodiversity Conservation: Healthy forests provide sanctuary to numerous species, ensuring genetic diversity and ecological resilience. Traditional techniques in forestry emphasize maintaining and enhancing this biodiversity.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests serve as significant carbon sinks, trapping carbon dioxide and mitigating climate change effects. Therefore, applying sustainable forestry techniques can help bolster carbon capture.
- Soil and Water Protection: Properly managed forests protect watershed areas, preventing soil erosion and preserving water quality. This maintains vital habitats and supports agricultural practices that depend on healthy soil.
By understanding these facets, one can appreciate how Calycanthus floridus fits within the broader forestry practice framework, especially concerning sustainable landscaping strategies.
Sustainable Forest Management
Principles of Sustainable Practices
Sustainable forest management emphasizes maintaining ecological processes while allowing for resource extraction. Some key principles include:
- Holistic Approach: Consideration of the entire ecosystem rather than focusing solely on timber production.
- Adaptive Management: Regularly updating practices based on the latest scientific findings and environmental conditions.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making processes to ensure that their needs are accounted for.
Techniques in Sustainable Management
Implementing sustainable techniques can vary greatly depending on the region and associated flora. For example:
- Selective Logging: This method minimizes damage to surrounding trees and promotes forest regeneration.
- Agroforestry: Integrating plants like Calycanthus floridus into agricultural systems boosts biodiversity while providing economic benefits.
- Restoration Projects: Planting native species is crucial in restoring degraded landscapes, thus enhancing ecological quality and resilience.
These sustainable practices play a vital role in ensuring that plants like Calycanthus floridus can thrive alongside other woodland flora.
Woodland Stewardship Strategies
Importance of Woodland Stewardship
Woodland stewardship involves actively managing forests and associated resources for health and sustainability. It is critical as it acts as a bridge between conservation efforts and community engagement. By taking a stewardship approach, landowners contribute to preserving native ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity.
Best Practices for Landowners
For those looking to manage their woodland areas effectively, consider the following practices:
- Regular Assessments: Monitoring tree health, soil conditions, and wildlife indicators can inform management decisions.
- Diverse Planting: Introducing a variety of species—including Calycanthus floridus—supports ecological resiliency and creates aesthetically pleasing landscapes.
- Community Involvement: Host workshops or community days to promote awareness and encourage collective action toward forest preservation.
"Healthy forests aren’t just a pretty sight; they are a testament to sustainable practices that benefit us all."
By incorporating these insights into maintenance strategies, landowners can contribute significantly to both conservation and community resilience.
Botanical Characteristics
The examination of botanical characteristics serves as the backbone of understanding the Calycanthus floridus. Exploring its unique taxonomy, morphological features, and growth habits not only unravels the essence of this shrub but also enables forestry professionals and conservationists to grasp its ecological footing. When discussing these facets, one can appreciate the distinctiveness and relevance of Calycanthus floridus in diverse landscaping and natural habitats.
Taxonomy and Classification
Calycanthus floridus, often referred to as the sweetshrub or carolina allspice, belongs to the family Calycanthaceae. This shrub has a unique position in the plant kingdom, primarily due to its early branching presence in angiosperm evolution. The genus name, Calycanthus, is derived from Greek, meaning 'beautiful flower' — a fitting title given its fragrant and striking blooms. The classification of this shrub typically includes:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Clade: Angiosperms
- Clade: Eudicots
- Clade: Magnoliids
- Order: Laurales
- Family: Calycanthaceae
- Genus: Calycanthus
- Species: C. floridus
Overall, understanding the taxonomy forms a crucial foundation for any further discussion on the species and its ecological role.
Morphological Features
Leaves and Foliage
The leaves of Calycanthus floridus are deciduous, providing a lush canopy that flourishes in the growing season. They are simple and elliptical, sporting a rich green color that can add depth to any landscape. A notable aspect is their aromatic quality when crushed, which can be appealing in a sensory garden or designated aromatic plant area. The high degree of leaf density allows for effective shade provision and moisture retention in the soil beneath. However, while the foliage showcases the shrub’s aesthetic appeal, it can also become a hassle when shedding in significant quantities during the fall, particularly in compact gardens.
Flowers and Fragrance
The act of blooming is where the flowers truly shine, with Calycanthus floridus offering large, cup-shaped blooms that can reach up to three inches across. The flowers bloom in a stunning mix of yellows, pinks, and browns, creating an eye-catching display in any garden. Its heady, cinnamon-like fragrance plays a major role in attracting both insects and birds, making it a favorite in pollinator gardens. However, one must consider that the blooms tend to appear later in the spring, which means they might not contribute to early-season pollinator needs.
Fruit Structure
The fruit structure of Calycanthus floridus also deserves mention. This shrub produces woody, capsule-like fruits containing several seeds that ripen in the fall. The fruits are not considered edible for humans, but they play a critical role in supporting wildlife. Birds and other small mammals can forage on these seeds, thereby contributing to the ecological cycle. The resilience of the fruit’s structure also allows it to survive harsh weather, although the shrub may not always produce abundant fruit in urban settings with limited pollinator access.
Growth Habits and Size
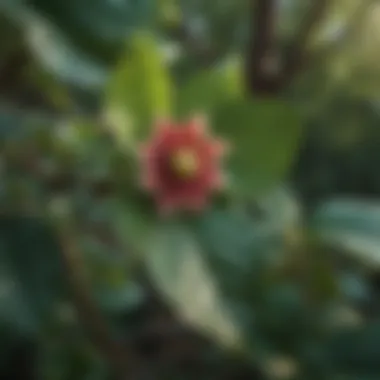

Calycanthus floridus typically grows as a multi-stemmed shrub reaching heights of six to ten feet, with a spread that can rival its height. Its bushy growth form can create a striking visual presence, either as a standalone focal point or as part of a larger planting scheme. Furthermore, with its ability to thrive in various conditions — including both moist and well-drained soils — it is generally regarded as a hardy option for diverse garden settings. The shrub also demonstrates a good tolerance for pruning, making it an excellent choice for controlled growth in urban landscaping.
Identifying and understanding these botanical characteristics yields valuable insights for implementing Calycanthus floridus into ecological restoration projects and enhancing urban biodiversity. The careful study of its taxonomy, morphology, and growth habits allows for informed decisions regarding its use in both public and private landscapes.
Distribution and Habitat Preference
The study of Distribution and Habitat Preference is essential for understanding Calycanthus floridus in its natural environment. Understanding where this plant thrives and the conditions it requires can aid in both its conservation and horticultural applications. This shrub is not just limited to any one area; instead, it dances across a variety of landscapes and climates, demonstrating its flexibility and resilience.
Geographical Range
Calycanthus floridus can be found predominantly in the southeastern United States. More specifically, its range extends from northern Florida and eastern Texas, up through Arkansas and into southern Illinois and Indiana. This distribution highlights its preference for warm, temperate climates, where conditions allow it to flourish.
Within this region, the plant is often located near streams and river banks, landscapes that provide adequate moisture and well-draining soils. It revels in the company of other native species, frequently found growing in understories of mixed hardwood forests. The geographical range of Calycanthus floridus not only defines its ecological niche but also influences conservation efforts aimed at protecting this species in its native habitats.
Preferred Ecological Zones
When it comes to ecological zones, Calycanthus floridus thrives predominantly in deciduous forests and woodland ecosystems. These areas are characterized by a rich tapestry of biodiversity, where varied plant and animal life coexists, contributing to a complex web of ecological interactions. The dense canopies and diverse understory provide a partial shade that is favorable for this shrub's growth.
The soil in these zones typically contains a mix of loam and sand, allowing for proper moisture retention without excessive waterlogging. Such environments support not just the physical growth of Calycanthus floridus, but also its role within the ecosystem by providing habitat and food for various species.
Adaptation to Soil Types
Calycanthus floridus showcases a remarkable ability to adapt to different soil types, a key factor in its success across various habitats. While it prefers moist, well-drained loamy soils, it has also been found in sandy or clay soils, demonstrating its versatility. Through natural selection, the plant has developed traits that allow it to deal with various soil conditions and moisture levels.
However, it is essential to note that extremes on either end of the soil spectrum—too dry or too saturated—can lead to stress for the plant. Adequate drainage is crucial, as waterlogged soils can promote root rot, threatening the plant's health. This adaptability highlights not only the ecological importance of Calycanthus floridus but its potential for use in landscaping, where diverse soil conditions may be present.
Understanding the distribution, habitat preferences, and adaptability of Calycanthus floridus is crucial for efforts towards its conservation and sustainable use in urban landscapes.
In summary, examining the distribution and habitat preference of Calycanthus floridus sheds light on its ecological role and potential applications in horticulture. This shrub is much more than a pretty face; its presence signifies a healthy ecosystem and a functioning biodiversity network.
Ecological Importance
Understanding the ecological importance of Calycanthus floridus vastly enhances its allure and resonates with its value within the ecosystem. This shrub not only beautifies spaces but also contributes significantly to the health and stability of local environments. Its ability to offer various ecological benefits, including supporting biodiversity and attracting necessary pollinators, paints a picture of a plant deeply intertwined with its biological community. Moreover, the role it plays in wildlife connectivity further solidifies its status as a keystone species in its native range.
Role in Biodiversity
The presence of Calycanthus floridus is a boon to biodiversity. This flowering shrub provides habitat for numerous species, both flora and fauna. By creating structured environments in gardens and natural areas, it supports diverse plant communities, which, in turn, sustain a wider array of wildlife. The shrub's lush growth offers shelter for smaller animals and insects, while its foliage serves as a backdrop for various understory plants. Such interactions are pivotal for ecosystem resilience and adaptability.
Attraction of Pollinators
Another significant benefit of Calycanthus floridus is its role in attracting pollinators. The fragrant, intricate flowers are particularly appealing to bees, butterflies, and other insects. These pollinators, in their search for food, inadvertently assist in the reproductive processes of surrounding flora by transferring pollen. This mutual relationship highlights the importance of the shrub in ensuring that interconnected plant species thrive, creating a vibrant tapestry of life in gardens and natural settings alike. The shrub's flowering period is crucial, as it offers sustenance when resources might be scarce, thereby retaining diverse pollinator populations.
Connection to Wildlife
Feeding Habitats
When discussing feeding habitats, Calycanthus floridus shines through its provision of sustenance for various wildlife. The fruit produced by this plant, though not the most commonly noted, can be a food source for small mammals and birds. Its seeds, often nestled in the fleshy fruits, become a nutritious meal for a variety of species. The shrub stands as a beneficial choice for local biodiversity, paving the way for complex feeding relationships. Its annual fruiting cycles also ensure that there's a steady food supply through different seasons.
Unique to this aspect is the relative scarcity of competition for these natural food resources, making Calycanthus floridus an excellent pick for supporting local wildlife.
Nesting Sites
The shrub serves as an important resource for nesting sites. Many birds find refuge and breeding grounds among its dense branches. This feature is essential, particularly in urban environments where natural nesting areas may be limited. The structural complexity of the plant provides an ideal setting for various bird species to safely raise their young, contributing to the overall stability of animal populations.
Furthermore, the shrub’s sheltered areas help protect nests from potential predators, offering a significant advantage for bird breeding success. Thus, it’s clear that Calycanthus floridus isn’t just a simple shrub; it plays an intricate role in the life cycles of various species, forging connections that extend far beyond its physical presence.
Cultivation and Horticultural Use
Understanding the cultivation and horticultural applications of Calycanthus floridus is essential not only for enthusiasts but also for those interested in sustainable landscaping and biodiversity support. This flowering shrub, known for its rich fragrance and attractive foliage, brings a unique aesthetic to gardens while also providing essential ecological benefits. Its versatility makes it suitable for various landscapes, from residential yards to public parks, all the while conforming to the local climate and soil conditions. The considerations that come with its cultivation are crucial for maximizing its benefits and promoting long-term health.
Planting Guidelines
When planting Calycanthus floridus, timing and location play significant roles. The best time to plant these shrubs is in the spring or fall, allowing roots to establish before extreme weather sets in. Choose a well-drained area that receives full sun to partial shade. Here's a quick rundown of the steps:
- Dig a Hole: Make a hole that is twice as wide as the root ball but only as deep as it is tall.
- Soil Preparation: Mix organic matter, like compost, into the soil to boost nutrients and improve drainage.
- Water Well: After planting, give the shrub a good drink to settle the soil and encourage root growth.
These simple guidelines help establish a firm foundation for future growth, ensuring that your shrub thrives.
Care and Maintenance
Calycanthus floridus, while resilient, does benefit from ongoing care. This includes proper watering and pruning strategies, which can greatly enhance its life and flowering capacity.
Watering Requirements
The watering requirements for this shrub are particularly noteworthy. During its establishment phase, consistent moisture is vital. However, it thrives in well-drained soils, so overwatering can be detrimental. In general, the shrub prefers deep watering once a week during dry periods. It's a delicate balance, and with a little observation, you can determine the right rhythm for your situation.
- Key Characteristic: Deep yet infrequent watering helps develop a robust root system.
- Advantages: By avoiding shallow watering practices, you're encouraging deeper root growth, which makes the shrub more drought-resistant in the long run.
Always check the soil moisture by sticking your finger an inch or two deep; if it's dry, it’s time to give it a drink.


Pruning Techniques
Pruning plays a vital role in the maintenance of Calycanthus floridus. Knowing when and how to prune can significantly affect its health and flowering potential. The best time for pruning is late winter or early spring, just before new growth begins.
- Key Characteristic: Light pruning encourages bushy growth and abundant blooms.
- Unique Feature: Unlike some shrubs, Calycanthus does not require heavy pruning; a gentle touch is all that’s needed to remove dead wood and maintain shape.
- Advantages: Regular, moderate pruning promotes air circulation within the bush, reducing the risk of disease while simultaneously enhancing its overall appearance.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitoring for pests and diseases is crucial for maintaining healthy Calycanthus floridus plants. Common pests include aphids and spider mites, which can be managed through natural predators or insecticidal soap. Furthermore, providing adequate spacing between plants will aid in air circulation, minimizing the risk of fungal diseases.
Healthy cultivation practices are central to the longevity and prosperity of your Calycanthus floridus plants, allowing them to thrive in both urban and natural environments.
Cultural and Historical Context
Calycanthus floridus holds an intriguing place in both cultural and historical realms. Acknowledging these dimensions deepens our knowledge about this flowering shrub and its significance beyond mere aesthetics. For generations, this plant has played a crucial role in various traditions and practices among different communities. Its flowering beauty and unique fragrance have shaped cultural narratives, making it much more than just another plant in the garden.
Understanding the cultural and historical context of Calycanthus floridus allows us to appreciate its value not just in ecological terms but also as a vessel of heritage and identity. This section delves into its traditional uses by Indigenous peoples, its symbolism found in literature and art, as well as its current cultural status.
Traditional Uses by Indigenous Peoples
In many Indigenous cultures throughout the southeastern United States, Calycanthus floridus, commonly known as sweetshrub, is more than just a shrub; it is embedded in cultural practices and medicinal traditions. The Iroquois and Cherokee people often used the leaves and bark of this plant for ceremonial and therapeutic purposes.
- Medicinal Uses:
- Ceremonial Importance:
- The bark was sometimes brewed into teas to relieve stomach ailments and fevers.
- The fragrant flowers were thought to aid in respiratory issues when inhaled.
- Sweetshrub was used in various rituals to encourage positive energies and ward off negativity.
- Its unique scent often played a role in healing ceremonies.
By understanding these traditional utilizations, it becomes clear how deeply rooted Calycanthus floridus is in the cultural tapestry of the Southeastern United States.
Symbolism in Literature and Art
The allure of Calycanthus floridus extends into literary and artistic representations. Writers and artists throughout history have captured its essence, emphasizing its significance within their works.
- Literature:
- Art:
- Authors often symbolize this shrub as a representation of resilience and beauty in nature.
- Its flowers appear in poems and novels, highlighting themes of renewal or nostalgia for simpler times.
- Many local artists depict the flowering shrub in paintings, embracing its aesthetic to evoke emotions related to spring's arrival.
- The use of Calycanthus floridus can be found in traditional crafts as well, often representing connection to past generations.
This rich symbolism not only enhances our aesthetic experience of the plant but also invites reflection on its broader meanings.
Current Cultural Significance
Today, Calycanthus floridus continues to resonate well beyond its ecological presence, influencing contemporary practices and environmental awareness.
- Sustainable Landscaping:
- Cultural Events:
- As interest in native plants grows, so does the appreciation for this shrub within sustainable landscaping. Homeowners and landscape designers opt for indigenous plants to promote local ecology, making sweetshrub a popular choice.
- Its hardiness and adaptability ensure that it can thrive in various urban environments, promoting biodiversity
- Festivals focusing on native plants often feature Calycanthus floridus, spotlighting its aesthetic and ecological benefits.
- Through workshops and community events, people reconnect with their heritage and learn to appreciate this native species.
In this way, the present cultural relevance of Calycanthus floridus reflects a consciousness about sustainability and local identity, forging a bridge between the past and the present.
"Calycanthus floridus is not only a beautiful addition to our gardens, but also a reminder of our deep-rooted connection to nature and heritage."
In summation, exploring the cultural and historical context of Calycanthus floridus enriches our understanding of this extraordinary shrub, reminding us of its intertwined narrative with the people and landscapes of the Southeast United States.
Conservation and Sustainability
The focus of conservation and sustainability regarding Calycanthus floridus is not just a passing trend. It arises from a necessity to protect a species that plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As climate change and urban development alter habitats, prioritizing the conservation of this plant becomes crucial.
Calycanthus floridus, also known as sweetshrub or Carolina allspice, requires attention due to its vulnerability to habitat loss. Whether it’s through urban sprawl or agricultural expansion, these changes directly impact the shrub's existence and the wildlife that relies on it. In light of this, creating awareness about sustainable practices becomes paramount.
The benefits of focused conservation efforts extend beyond the plant itself; they also foster biodiversity, enhance community green spaces, and contribute positively to local economies. Organizations and communities can work together to ensure enduring practices that promote the health of both Calycanthus floridus and its ecosystem.
Threats to Natural Populations
Calycanthus floridus faces multiple threats, primarily linked to environmental degradation and habitat destruction. Some of the primary factors include:
- Urban Development: As cities grow, natural spaces are sacrificed for infrastructure, significantly reducing the natural habitats of this shrub.
- Invasive Species: The presence of aggressive non-native plants can quickly overshadow Calycanthus floridus, competing for sunlight and nutrients.
- Climate Change: Fluctuating weather patterns can alter the suitable growth areas for this species, potentially making current habitats less viable.
These challenges signal a pressing need for action. Without intervention, the future prospects of Calycanthus floridus and its role in the ecosystem may diminish.
Conservation Efforts
Local Initiatives
Local initiatives have become a beacon of hope for preserving Calycanthus floridus. Community-driven projects emphasize the importance of native plants in local landscapes. These initiatives often focus on:

- Education: Informing the public about the ecological benefits of sweetshrub encourages native plant gardening.
- Restoration: Many local groups undertake specific restoration projects to rehabilitate areas where Calycanthus floridus has declined.
A key characteristic of these initiatives is grassroots participation. They foster community engagement and instill a sense of ownership over local flora. One unique feature is the collaboration between local nurseries and conservation groups, giving citizens easy access to native plant varieties that support local biodiversity. However, challenges include securing consistent funding and volunteer participation, which can fluctuate over time.
Partnerships with Environmental Organizations
Forming partnerships with environmental organizations represents another significant stride toward the conservation of Calycanthus floridus. Such collaborations magnify efforts by pooling resources, expertise, and outreach capabilities. These partnerships typically bring together:
- Scientific Knowledge: Environmental organizations often have researchers dedicated to understanding the needs of native species like sweetshrub.
- Advocacy Platforms: Partnering enhances the visibility of these species in conservation discussions, rallying support from policymakers.
A standout feature of these partnerships is their ability to enact broader public policies that protect native species’ habitats. They often engage in efforts that go beyond mere protection—such as promoting active restoration strategies. A potential disadvantage might be bureaucratic delays, which can sometimes hinder timely action.
Promoting Sustainable Practices
Encouraging sustainable practices involves both community engagement and education regarding responsible horticulture. To sustainably incorporate Calycanthus floridus into landscaping, consider:
- Planting Guidelines: Implementing specific guidelines for integrating this shrub into urban designs can facilitate its success. Proper spacing, soil amendments, and watering practices optimized for this plant help it thrive.
- Public Workshops: Hosting informational sessions about the ecological importance of native species can enlighten individuals about their landscaping choices.
- Continuous Support: Offering resources and support to individuals and organizations attempting to incorporate Calycanthus floridus ensures sustained interest in its conservation.
Through these practices, communities can contribute to the longevity and health of Calycanthus floridus, ensuring that this charming shrub continues to flourish in both wild and cultivated settings.
Potential for Urban Landscaping
Calycanthus floridus holds considerable promise for urban landscaping, offering unique aesthetic qualities and ecological advantages. Planet Earth is increasingly facing urban sprawl, taking its toll on natural environments. Therefore, incorporating native plants like Calycanthus floridus provides a pathway to creating sustainable urban ecosystems. This shrub is not just about looks; it's a multifunctional asset that can enhance both the visual and environmental aspects of urban environments.
Aesthetic Value in Design
Calycanthus floridus, often known as the sweetshrub, showcases a remarkable aesthetic appeal. Its foliage adds a lush green blanket to landscapes, while the flowering stage offers intoxicating, fragrant blooms. These flowers, which often carry a charming cup-shape, can transform any urban garden into a floral haven.
- Its striking, reddish-brown flowers bloom from late spring to early summer, likening their appearance to delicate, crumpled silk.
- The aromatic nature of the blooms can create a sensory experience that enhances outdoor spaces, inviting both people and pollinators.
- Additionally, the shrub grows to a height of around six to ten feet, making it versatile for various design setups—whether used as a hedge or focal point in a garden bed.
Integrating Calycanthus floridus into urban designs speaks to the growing trend of biophilic design, which emphasizes the connection between people and nature through visual and sensory experiences.
Benefits for Urban Biodiversity
In the context of urban environments, biodiversity is vital for ecosystem health. Calycanthus floridus can play a significant role in enhancing urban biodiversity. Its native status allows it to thrive in local conditions while providing crucial habitat for various species:
- Pollinators: The fragrant flowers attract bees, butterflies, and other insects, supporting local pollinator populations.
- Wildlife: Birds and various small mammals find refuge in the dense foliage, creating a living tapestry of urban biodiversity.
- Soil Health: As a deciduous shrub, it contributes organic matter to the soil when leaves fall, fostering soil health and fertility.
As cities continue to evolve, integrating species like Calycanthus floridus can counterbalance the loss of natural habitats, leading to richer, more diverse urban ecosystems.
Case Studies of Successful Planting
Several urban spaces have embraced Calycanthus floridus as part of their landscaping strategy, and the outcomes speak volumes. In various cities, successful installations have demonstrated the viability of this plant:
- Central Park, New York City: Urban planners introduced Calycanthus floridus into several garden areas, emphasizing its fragrant blooms. This initiative has not only beautified the space but also attracted diverse pollinators, which had been declining in the area.
- San Francisco's Golden Gate Park: This initiative focused on using native shrubs for a more resilient ecosystem. The sweetshrub’s adaptability to the soil types and its drought resistance made it a prime candidate. Visitors now enjoy a fragrant walking path active with wildlife.
- Atlanta's BeltLine:
As part of a larger initiative to transform old railway lines into parks, local authorities featured Calycanthus floridus in open spaces. The success here highlights how integrating local flora can help promote sustainable practices in urban development.
In these cases, Calycanthus floridus has proven to be an excellent addition, enhancing not just the aesthetics but also promoting healthy ecosystems.
"The integration of native plants into urban landscapes is no longer a recommendation but a necessary strategy for sustainability and resilience."
Future Research Directions
The study of Calycanthus floridus opens avenues for research that can illuminate both its ecological role and practical applications. Understanding future research directions is crucial not only for conservation but also for maximizing the plant's benefits in diverse settings. This shrub, deeply rooted in the ecosystems of the southeastern United States, presents various aspects worth exploring.
Genetic Studies for Conservation
One primary element in future research involves genetic studies aimed at conservation. By investigating the genetic diversity of Calycanthus floridus, researchers can gain insights into its adaptability to various environmental stressors, including disease and climate change. Researching genetic markers can provide information on population structure and dynamics, which are fundamental to effective conservation strategies. Moreover, understanding the genetic makeup can facilitate the development of breeding programs aimed at increasing resilience.
- Benefits of Genetic Studies:
- Increased understanding of genetic variation and adaptations.
- Development of conservation policies rooted in scientific evidence.
- Potential to enhance the plant’s medicinal properties through selective breeding.
By using advanced techniques like genome sequencing, researchers can uncover how this shrub reacts to different conditions. This knowledge not only aids conservationists but could also enrich horticultural practices, ultimately benefiting the larger ecosystem.
Exploring Medicinal Properties
Another exciting path lies in exploring the medicinal properties of Calycanthus floridus. Traditionally used in folk medicine, the potential health benefits of this plant beckon the interest of scientists. Evaluating its chemical compounds might reveal anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial properties, previously noted but not fully substantiated through rigorous research. There’s potential in examining the essential oils extracted from the flowers and leaves—perhaps they contain bioactive compounds that promote human health.
- Reasons for Exploration:
- Historical Significance: Indigenous cultures have long valued this shrub for various remedies.
- Modern Application: Could lead to the development of new herbal supplements or pharmaceutical products.
- Contribution to Biodiversity: Encourage conservation while promoting sustainable harvest practices that safeguard the species.
A focused research effort on this front could also stimulate economic activity, benefiting both local communities and researchers alike.
Impacts of Climate Change on Distribution
The final research avenue to consider is the impact of climate change on the distribution of Calycanthus floridus. As climate patterns shift, the habitats suitable for this species may alter as well. Understanding those changes requires a comprehensive approach that analyzes how temperature fluctuations, precipitation variations, and changing soil conditions affect plant growth and reproduction. Assessing this shrub’s responses to changing climate conditions will be key to predicting its future in native and non-native environments.
"The adaptability of Calycanthus floridus in the face of climate change may very well determine its long-term survival and role in local ecosystems."
- Focus Areas:
- Monitoring geographic shifts in populations over time.
- Examining interactions with other species influenced by climate change.
- Predictive modeling to ascertain which new habitats could support the plant in the future.
By integrating ecological modeling with field data, researchers can build a comprehensive picture of how changes in our environment might threaten or promote the survival of Calycanthus floridus.







