Tree Spur Climbing Kits for Sustainable Forestry

Intro
Tree spur climbing kits form a critical part of effective forestry practices. As the demand for sustainable management of woodland resources grows, it becomes paramount for professionals in the field to equip themselves with both knowledge and the right tools. These kits not only enhance safety when navigating trees but also support effective woodland management strategies that impact ecosystems positively.
In this discussion, we will delve into the multifaceted world of tree spur climbing kits, examining their components and functionalities. Our focus will include essential insights on selecting the best gear, adhering to safety protocols, and maintaining equipment effectively. Furthermore, we will explore the integration of technology that can aid in climbing techniques, which leads to a broader understanding of fostering sustainability in forestry.
The role of tree spur climbing cannot be overstated; it opens up access to tree canopies, allowing for assessment, research, and management interventions that are crucial for healthy forest ecosystems. Moreover, as forest professionals and enthusiasts alike navigate the complexities of woodland stewardship, understanding the intricacies of climbing gear and its applications can significantly enhance their operational efficiency.
As we embark on this journey through the essential insights related to tree spur climbing kits, it is essential to recognize their role in supporting sustainable forest management practices and promoting responsible stewardship of our natural resources.
Prelims to Tree Spur Climbing
Tree spur climbing is more than just a technique; it’s an art that intertwines with the broader practice of forestry. Whether one is an enthusiast hoping to enjoy nature from its highest points, or a professional needing access for evaluating tree health, understanding the nuances of tree spur climbing can enhance both the experience and effectiveness. This article explores essential insights into tree spur climbing kits, emphasizing their components, safety considerations, and best practices. The significance of these climbing kits lies not only in facilitating effective climbing but also in ensuring the climber's safety, which is paramount in forestry work where conditions can be unpredictable.
Understanding the Basics of Climbing
Tree climbing, particularly using spurs, requires a firm grasp of fundamental techniques. These basics include mastering balance and gaining proficiency in installing spurs onto the tree, as improper placement can be risky. Climbers need to build stamina and strength since scaling heights can be physically demanding. The respect for the tree and the environment is also vital; a climber must understand how their actions can affect the health of the forest. Knowledge of different tree species and their bark characteristics further enriches a climber's effectiveness in the field.
Overview of Tree Spur Climbing Kits
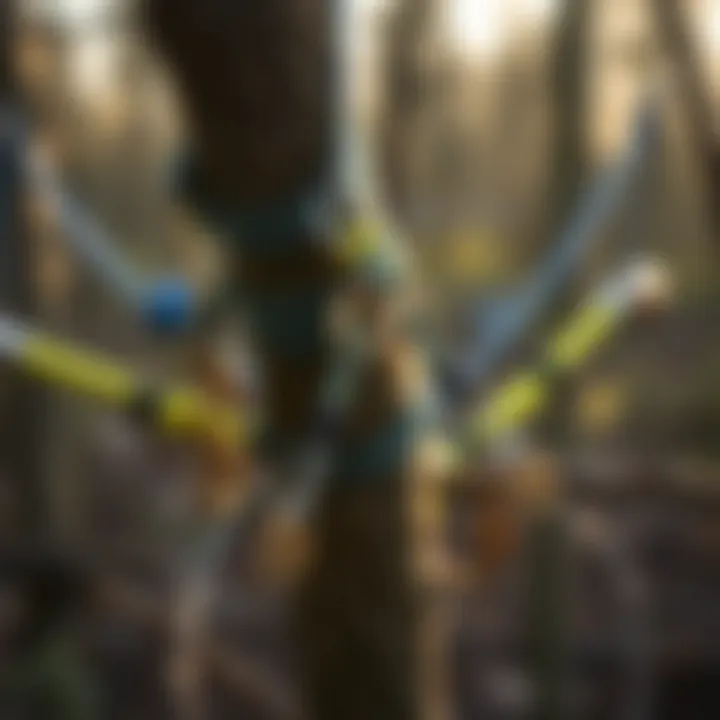
Tree spur climbing kits are specialized collections of gear designed to assist climbers in ascending trees safely and efficiently. These kits typically include spurs, a climbing harness, lanyards, and additional safety accessories like helmets and gloves. The various components work cohesively, ensuring that climbers maintain a secure hold while navigating heights.
When exploring tree spur kits, one must pay attention to key features such as the materials used in spurs, which can affect weight and durability. Metal spurs, for example, offer robustness but may weigh more than their plastic counterparts. Adjustable spurs can provide flexibility for different leg sizes, increasing comfort and safety. As climbers gain experience, they may also seek kits that include advanced elements like shock-absorbing lanyards which can cushion falls, a critical consideration in any climbing endeavor.
"A good tree climbing kit is like a trusty companion; it ensures you are prepared for the heights and challenges that lie ahead."
Components of a Tree Spur Climbing Kit
Understanding the components of a tree spur climbing kit is essential for anyone involved in forestry practices. Every bit of gear plays a distinct role in ensuring safety and efficiency. By knowing what each element contributes, climbers can make informed choices that enhance their overall climbing experience.
When selecting a kit, it’s vital not just to have the right tools but also to know how they interact. A well-rounded kit includes spurs, climbing harnesses, lanyards, ropes, and safety gear, each intertwined in function and purpose. This ensures climbers can scale trees effectively while minimizing risks.
Types of Spurs
Spurs, which are attached to the climber's boots, are indispensable for gaining traction on tree trunks. They come in various materials, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right type will greatly influence the climbing experience.
Metal Spurs
Metal spurs are often the go-to choice for professionals who need durability. Made from robust materials, these spurs can withstand repeated wear and tear while providing excellent grip. The key characteristic of metal spurs is their sheer strength and support, making them a preferred option for climbers working on larger trees.
One standout feature of metal spurs is their longevity. Climbers who invest in high-quality metal spurs often find they can last several seasons with proper care. However, they can be heavy and may cause fatigue during extended climbs.
Plastic Spurs
On the flip side, plastic spurs are gaining popularity, especially among those who favor lightweight equipment. Their reduced weight makes them easy to handle, which is particularly appealing for long climbs or for those who may not have as much upper body strength.
Plastic spurs also tend to be softer on the tree bark, helping to preserve it from excessive damage. However, while they are less cumbersome, they may not hold up as long against rough surfaces or more challenging climbing conditions.
Adjustable Spurs
Adjustable spurs bring a level of versatility that is hard to dismiss. These spurs allow for a customizable fit, accommodating various boot sizes and preferences. This adaptability makes adjustable spurs a favorite choice among teams with multiple users or across different climbing contexts.
Their unique feature is the capability to modify the size of the spur, ensuring a snug fit for maximum comfort. However, they may require more maintenance to ensure the joints and adjustments remain functional over time.
Climbing Harness
An effective climbing harness is vital, serving as the backbone of the climber's safety system. It distributes weight evenly, offering comfort during long, strenuous climbs. A well-designed harness allows the climber to maneuver easily, thus facilitating access to even the highest branches without compromising safety.
There are various types of harnesses, from traditional designs to more modern, ergonomic ones. The ideal harness should provide ample padding for comfort while maintaining a snug fit to prevent any unwanted slips or movement.
Lanyards and Ropes
Lanyards and ropes play a critical role in maintaining connectivity to the tree. Ropes are usually the lifelines, literally, as they allow for controlled descent and ascent. Lanyards add that extra security, ensuring the climber is anchored correctly while working.
Choosing the right ropes involves considering their strength, elasticity, and grip. Many climbers opt for dynamic ropes, which offer some stretch to absorb the shock of falls, while static ropes are favored for anchoring securely. Lanyards, whether pre-tied or adjustable, should always adhere to safety standards ensuring they can bear the climber's weight during peak loads.
Safety Gear
Safety gear comprises the protection that climbers need while scaling trees. It is crucial to emphasize its importance. Equipment like helmets, gloves, and knee pads significantly reduce the likelihood of injury during climbs.


Helmets
The role of helmets cannot be overstated. They provide indispensable protection against falling debris and other potential hazards from tree climbing. A strong helmet absorbs impacts, helping to prevent serious injuries. Most options today are designed to be lightweight yet strong, ensuring that climbers don’t feel burdened while maintaining safety.
Gloves
Climbing gloves protect the hands, providing a buffer against sharp bark and abrasive surfaces. A good pair enhances grip, which can decrease slippage while there's a physical advantage during the climb. Yet, depending on the material, gloves can diminish tactile sensitivity, which may be crucial for some climbing tasks.
Knee Pads
Knee pads offer a layer of protection for the knees, particularly important during prolonged periods spent climbing or when making contact with surfaces that could lead to scrapes and bruises. They’re often made from soft materials suitable for comfort but should be sturdy enough to withstand repeated usage.
Ultimately, investing in a comprehensive tree spur climbing kit, knowing each component, and recognizing its importance lays the groundwork for effective and safe climbing practices.
Selecting the Right Climbing Kit
Choosing the right climbing kit is do or die in the business of tree climbing. Not just any set of gear will cut it in the wild, and what you pick can dictate not only your efficiency up there but also, and more crucially, your safety. This section unpacks the bits and pieces you need to think about when selecting a climbing kit, ensuring that it aligns with both your needs and the trees you'll be tackling.
Factors to Consider
When it comes down to making the right choice, a few key considerations stand out. Let's dive into these aspects one by one.
Type of Trees
The choice of trees you're dealing with has big time implications for your climbing kit selection. Imagine you are scaling a sturdy oak versus a nimble pine—these trees vary quite a bit in terms of their bark and overall structure. In forestry, many practitioners favor climbing on oaks, known for their reliability and toughness.
The key characteristic of various trees lies in their bark texture and height. Some trees, like maple, sport smoother bark that might make footing tougher, while hardwoods like oak can offer better traction for spurs. The unique feature to keep in mind is the height and branch structure; branches that fan out wide make for easier access, but those high, narrow trunks can require specially designed gear to climb safely. Choosing the right gear can enhance your efficiency and help reduce fatigue while climbing. Every trek is different, and knowing your environment is half the battle.
Climber’s Experience
Experience is another make-or-break factor. A seasoned climber is likely to have a different set of priorities compared to someone who just entered the game. More seasoned climbers often seek out specialized gear that can handle complex climbs and give them an edge on difficult terrain. This consideration can steer you away from entry-level kits geared towards beginners.
The distinct feature here is that experienced climbers generally have a better understanding of how gear interacts with their body and the tree, allowing them to select more specialized kits. If you’re just starting out, you might prefer a comprehensive kit that offers simplicity and guidance on safe practices. Going for options that prioritize ease of use can speed up your learning curve, but sometimes they lack the flair required for advanced maneuvers. Balancing proficiency with learning is crucial.
Budget Constraints
Then there's the matter of budget. You could have the fanciest gear around, but if it stretches your wallet too thin, it’ll become a burden instead of a blessing. As with any investment, it’s about ensuring you’re getting bang for your buck without skimping on quality.
A decent climbing kit doesn’t necessarily mean you need to fork out all your savings. Many brands provide quality options that won’t burn a hole in your pocket, allowing you to focus on tree tackling instead of worrying about finances. The unique feature here is the range available; you can find good mid-level kits that hold up during most climbs and keep your expenses in check. Ultimately, it’s about finding a balance between safety and cost. Don’t cut corners when it comes to crucial gear, but you also can avoid high-end products that don’t offer significant benefits.
Brand Comparisons
Not all climbing kits are created equal—different brands cater to various needs, budgets, and preferences. For instance, brands like Petzl are often revered for their durable gear that withstands the test of time, while Marlow may offer excellent value without compromising safety.
When weighing brands, it’s essential to consider:
- User Feedback: Look for reviews from peers in the forestry community. They serve as real-world testimonials of how gear functions in the field.
- Durability: Some brands have a reputation for sturdiness built over many years, while others might be another flash in the pan.
- Innovation: New features can make climbing easier, but not all innovations translate to effective solutions. Take time to consider if the gimmicks truly enhance your climb or merely serve as a marketing tool.
In summary, selecting the right climbing kit isn't merely about what looks good on the shelf. It’s about understanding your surroundings, your experience level, budget constraints, and the brands that can support your adventures in tree climbing.
Techniques for Effective Climbing
Understanding the various techniques for climbing trees with spur kits is crucial for both safety and efficiency in forestry practices. The right techniques not only enable climbers to ascend and descend with stability but also minimize the risk of accidents, ensuring the climber can focus on the task at hand. With a variety of techniques available, it’s essential to choose what best suits the climbing environment and the individuals' skill level. Following a systematic approach can significantly enhance productivity and effectiveness in woodland management tasks.
Basic Climbing Techniques
Basic climbing techniques serve as the foundation for any climbing endeavor. They involve the fundamental movements and practices that every climber should master before progressing to more advanced methods. A few key components include:
- Proper Use of Spurs: Ensuring that the spurs are securely fastened to the climber's boots helps provide stability when ascending. It is crucial to maintain a firm grip throughout the climb.
- Body Positioning: Keeping the body close to the trunk of the tree allows for better balance and control. The climber should utilize their legs to push upward rather than relying solely on arm strength.
- Three-Point Contact: Maintaining three points of contact at all times enhances safety. For example, having two feet on the trunk while one hand grips a branch can help prevent falls.
Focusing on these elements can ease the learning curve for novice climbers while also refining the skills of more experienced individuals.
Advanced Climbing Techniques
Advanced climbing techniques elevate the climber's ability to maneuver through complex environments efficiently. These techniques require practice and familiarity with the climbing gear but can provide significant advantages in various climbing scenarios.
Footlocking
Footlocking is a climbing technique that involves using the feet to secure a position on the rope. This technique allows for effective ascent without the need for upper body strength solely. The key characteristic of footlocking is its reliance on a solid anchor point created by the feet, offering stability while climbing higher in the tree.
- Advantages: Footlocking enables climbers to conserve energy, as it requires less effort from the upper body. It also provides climbers with a method to ascend relatively rapidly through the rope system, beneficial in tasks that require quick positioning.
- Disadvantages: On the flip side, footlocking might not be suitable for every climber, especially for those with limited foot dexterity or strength. Furthermore, improper technique can lead to slips or falls if not executed correctly.


Butterfly Technique
The Butterfly Technique is another sophisticated climbing maneuver that allows for efficient rope management and movement up the tree. The key characteristic of this method is its unique method of utilizing both ropes for stability and support during the climb.
- Advantages: The primary advantage of the Butterfly Technique is its adaptability. Climbers can easily alter their position without having to change the anchor points significantly. This can be particularly helpful in dense tree canopies where maneuvering is often required.
- Disadvantages: However, this technique also comes with challenges. It can be somewhat complex to master for beginners, as it requires a nuanced understanding of how to manage both the climbing gear and body movements effectively. Additionally, inexperienced climbers might find it initially disorienting.
Mastering both basic and advanced techniques can dramatically improve climbing proficiency, helping to ensure that woodland management tasks are performed efficiently and safely.
Safety Considerations in Tree Climbing
Tree climbing, particularly with tree spur kits, is no walk in the park. Safety considerations are of utmost importance for any climber, be it a novice or a seasoned professional. Each ascent comes with its own set of risks, and ignoring safety guidelines can lead to severe consequences. Focusing on safety not only protects the climber but also enhances the overall effectiveness of forestry practices.
Understanding Risks
Tree climbing involves various risks that can stem from multiple factors, such as:
- Equipment Failure: If your gear is worn out or improperly used, it can fail. Regular checking of spurs, harnesses, and lanyards is a must.
- Environmental Hazards: Trees can harbor dangers like falling branches or nests of wasps. Being aware of your surroundings is crucial.
- Physical Strain: Climbing puts stress on your body; improper technique can lead to injuries. Maintaining fitness and practicing correct movements cannot be overlooked.
By comprehending these risks, climbers are better equipped to mitigate them. Risk awareness leads to more informed decision-making while climbing, which ultimately contributes to safe and effective forestry practices.
Pre-Climb Safety Checks
Before venturing into the canopy, a thorough safety check can be likened to double-checking your recipe before cooking. A few minutes of preparation can save plenty of distress later on.
Key items to inspect include:
- Gear Condition: Look for any frayed ropes, rusted spurs, or wear on the harness. Anything that looks past its prime could put you at risk.
- Climbing Path Assessment: Analyze the tree you plan to climb. Are there any visible dangers? Is the trunk stable?
- Weather Conditions: Windy days can turn a climb into a hair-raising experience. It’s best to avoid climbing in bad weather, and always have a backup plan.
Doing a pre-climb safety check is as essential as the climb itself. It's all about ensuring you are prepared and set up for success.
Emergency Preparedness
In the world of climbing, it’s better to have a plan and not need it than to find yourself in a predicament without one. Emergency preparedness goes hand in hand with climbing safety. Here are some essential components:
- First Aid Kits: Always have a first aid kit with basic supplies like bandages, antiseptic wipes, and tape.
- Communication Devices: Carry a mobile phone or a walkie-talkie. In case of emergencies, reaching out to someone nearby can make all the difference.
- Emergency Contacts: Make a list of emergency contacts and ensure someone knows your climbing plans. This way, if something goes awry, assistance can arrive more promptly.
Remember: A good climber isn’t simply someone who can ascend a tree; it’s someone who prepares for both the ascent and potential descent into difficulties.
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure."
Maintaining Climbing Gear
Maintaining climbing gear is not just a best practice but a necessity for anyone involved in tree spur climbing. This involves ensuring that all components of a climbing kit are in optimal condition. Proper maintenance can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance the life span of the gear, allowing climbers to perform their tasks effectively and safely. By focusing on regular inspections and efficient cleaning and storage methods, climbers follow best practices that ultimately contribute to better woodland management.
Regular Inspections
Inspecting climbing gear regularly is like oiling the gears of a fine machine. It helps you spot wear and tear before it becomes a bigger issue. Climbers should adopt a habit of performing these checks routinely. Here are some critical aspects to consider when conducting inspections:
- Examine Spurs: Look for any cracks or signs of bending. A damaged spur can lead to a fall.
- Check Harnesses: Inspect the buckles, webbing, and stitch lines for any fraying or degradation.
- Lanyards and Ropes: Ensure that there are no cuts or abrasions. Even a small tear can compromise safety.
- Safety Gear: Helmets and gloves should be checked for any signs of impact or dirt buildup, which could indicate less protection.
Mark the date of each inspection on a log. This helps in tracking the wear and tear over time. An organized approach reinforces a methodical mindset towards safety. The importance of keen observation cannot be overstated; a climber's life may depend on it.
Cleaning and Storage
After a long day of climbing, it's often tempting to toss gear in a corner and forget about it until the next use. However, neglecting cleaning and proper storage can have long-lasting consequences. Here are some practices that enhance the durability of climbing equipment:
- Cleaning Gear: After use, give your spurs, harness, and ropes a gentle wash with mild soap and water. Dirt and sap can degrade materials over time. For ropes, a soak in clean water helps remove any trapped debris.
- Drying: Always allow your climbing gear to dry completely before storing it away. Mold and mildew can develop on damp equipment, posing risks for health and safety.
- Organized Storage: Store harnesses and ropes in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Hanging them on hooks can prevent tangling and maintain their shape. Spurs can be placed in a sturdy container to avoid crushing or bending.
Proper maintenance reduces risks while maximizing the lifespan of climbing gear. Knowing how to take care of your equipment is as crucial as the climbing techniques you employ.
By adhering to these practices, climbers show a commitment not just to their own safety but also to the stewardship of the forests they work within. Taking these steps assures that climbing gear remains reliable and efficient, ultimately paving the way for better forestry practices.
Alternative Climbing Practices
In the realm of forestry, alternative climbing practices diversify the options available to climbers and can significantly enhance safety and efficiency in tree management. These methods by-pass some limitations of traditional climbing techniques, often offering unique advantages for both the trees being climbed and the climbers themselves.
Natural Climbing Techniques
Natural climbing techniques draw from skills honed through observing wildlife and understanding the environment. This method employs the climber’s body in conjunction with the tree itself, allowing for a more intuitive ascent. Unlike mechanical methods, these techniques emphasize connection with the tree, minimizing equipment use while maximizing skill and adaptability.


- Foot Placement:
- Body Positioning:
- Branch Assessment:
- Proper foot placement on branches and trunk ensures stability and reduces fatigue. Climbers often rely on their legs more than arms, which is key.
- Utilizing one's center of gravity effectively can make climbing smoother. For instance, leaning towards a branch strengthens grip while distributing weight evenly.
- Understanding the health of branches is crucial. A natural climber learns to identify which limbs are strong enough to bear their weight and which should be avoided.
Natural climbing fosters a deep respect for the ecosystem. It encourages climbers to remain observant and aware, honing skills that can be only developed through practice. However, climbers should be aware of their physical limitations and be trained appropriately before attempting these techniques to avoid accidents.
"A tree's architecture can be more forgiving than you think; listen to it, and it will guide your climb."
Mechanical Advantage Systems
Mechanical advantage systems introduce an innovative aspect to climbing that can dramatically increase efficiency. These systems use pulleys and other mechanical means to distribute weight and reduce the effort required to ascend and descend trees.
- Pulleys:
- Prusik Knots:
- Progress Capture Devices:
- These allow climbers to reduce the load on the body. By rerouting the rope through a pulley, climbers can create a system that allows them to work with less effort while carrying gear or other loads.
- These serve as a friction hitch and allow for a more secure positioning while climbing. The double-clutch nature of the knot gives climbers the ability to ascend without worrying about slipping back.
- This is a key component; they allow a climber to ascend smoothly while automatically locking the line, thereby offering reserving safety in case of slips.
While mechanical systems can offer safety and efficiency, they also come with more complexity. Climbers need to be informed and well-practiced in employing these systems effectively. Understanding how to set up and use mechanical equipment can take time, but it is often well worth the investment.
Both natural techniques and mechanical advantage systems play vital roles in effective tree climbing practices. Choosing one over the other can depend on personal preference, the particular tree, and specific objectives relating to the task at hand. Engaging with both methods can expand a climber’s toolbox, enhancing their ability to perform in diverse conditions.
Technological Integration in Climbing
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving forestry environment, the integration of technology into climbing practices offers significant advantages for both professional arborists and enthusiasts alike. This includes improved safety, efficiency, and overall effectiveness in managing tree services. As we delve deeper into the innovation that surrounds tree spur climbing kits, understanding the role of technology highlights key aspects that not only streamline the climbing process but also ensure safety standards are met.
Innovative Gear Features
When considering modern climbing gear, numerous innovative features come to light that elevate the climbing experience. With an eye on user experience, manufacturers have been adding technology-infused elements to traditional spurs and harnesses. Here are some noteworthy advancements:
- Lightweight Materials: Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating lightweight yet durable composites that decrease fatigue on long climbs, allowing for a more comfortable experience.
- Enhanced Grip Systems: Advanced spurs now come equipped with specialized designs that provide better grip on various tree species. This might include textured surfaces or interchangeable spikes designed for specific conditions.
- Integrated Safety Features: New designs boast safety mechanisms like automatic locking carabiners that minimize the risk of accidental release. Climbing harnesses also now often include impact indicators, helping climbers quickly assess whether their gear remains viable after a fall.
- Modular Components: The ability to customize gear through modular components allows climbers to adapt their kits based on the tree species or environmental challenges they face. This flexibility serves to enhance both comfort and safety.
"Investing in high-quality climbing gear with the latest technological features can significantly impact your climbing safety and efficiency. It’s not just about the ascent; it’s about doing so with confidence."
Smartphone Applications for Climbers
In the digital age, smartphones have transformed how climbers approach their responsibilities. Numerous applications are available that cater specifically to the needs of forestry professionals. Here’s how these apps can aid in climbing practices:
- Climbing Path Planning: Apps like 'Tree Climbing Planner' help climbers visualize their ascent, allowing for better route selection and efficiency.
- Weather Forecasting: Knowing how weather conditions can change rapidly is crucial. Applications offering real-time weather updates prevent climbers from getting caught in unexpected storms or dangerous wind conditions.
- Emergency Communication: Many apps feature SOS buttons or emergency contact options, which can be lifesavers in critical situations. Immediate access to emergency services adds a reliable layer of safety.
- Performance Tracking: Climbers can utilize apps to log their climbs, track their performance over time, and share their experiences with fellow climbers. This not only provides benchmarks for improvement but also fosters a sense of community.
In sum, the technological integration in climbing not only enhances performance and safety but offers climbers tools that promote smarter and more efficient climbing. As these technologies evolve, they stand to redefine what it means to climb trees effectively in sustainable forestry practices.
Finale and Further Reading
In wrapping up, the discussion on tree spur climbing kits delves into the core of not just climbing but the broader context of forestry practices. As professionals in this field, understanding the essence of these kits is vital. They are not merely tools; they represent a safe and efficient approach to working with trees - vital for both ecological integrity and personal safety.
The integration of various components, such as spurs, harnesses, and safety gear, underscores the importance of selecting equipment tailored to one's specific needs. Moreover, it’s essential to constantly revisit best practices in emphasizes a continuous learning approach. Each tree presents its unique challenges and insights, and understanding these can significantly elevate the quality of work undertaken.
While climbing techniques have their nuances, safety considerations stand paramount. Each climber bears the responsibility to perform pre-climb checks and maintain their gear meticulously. This diligence not only safeguards the climber but also contributes to sustainable forestry by minimizing risks that could lead to accidents.
Furthermore, the ever-evolving technology in gear design and smart applications serves as a testament to the profession’s commitment to growth and development. This integration can streamline processes, keep climbers connected, and enhance the overall experience in tree climbing.
The importance of continuous education in this discipline cannot be overstated. As you pursue further understanding and resources, consider the recommended practices and resources available. The knowledge acquired propels you to become not just a better climber but an informed steward of the environment.
"In forestry, knowledge isn't just power; it’s a pathway to responsible stewardship and effective practices."
Summarizing Best Practices
In summary, best practices in tree spur climbing hinge on several key elements:
- Choose the Right Gear: Prioritize quality and suitability based on your needs.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your climbing kit in top shape with regular inspections and proper storage.
- Safety First: Implement strict safety checks before every climb to avoid potential hazards.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with advancements in climbing techniques and equipment.
These practices not only enhance climbing efficiency but also ensure compliance with safety regulations, minimizing accidents.
Recommended Resources
For further exploration, consider diving into the following resources:
- Wikipedia on Tree Climbing
- Britannica’s Overview on Forestry
- Engage with communities on Reddit's Forestry Subreddit
- Follow discussions on Facebook Forestry Groups
By tapping into these resources, you can enhance your understanding of the field and stay abreast of best practices and innovations that arise within the realm of tree spur climbing while also keeping your approach fresh and informed.







